- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
- Share on X
- Share on WhatsApp
- Share on Viber
- Share on Threads
- Share on Reddit
Table of Contents
Introduction
Running successful Google Ads campaigns requires more than selecting the right keywords and setting a budget. From individual advertisers to large marketing teams, many aren’t using the full capabilities the platform provides.
Understanding and applying the right Google Ads features can help bridge the gap between overspending and building an efficient, high-performing acquisition strategy. With Google Ads reaching over 90% of internet users, knowing how to use its core functions effectively can offer a real advantage.
Focusing on these areas can help you:
- Increase return on ad spend (ROAS)
- Improve clickthrough rates (CTR)
- Minimize common campaign inefficiencies
We break down ten features that are frequently overlooked but have a measurable impact on results. Each one is practical, adjustable, and worth revisiting — whether you’re managing a single account or many.
1. Why your ad might not show even when you win the auction
Many advertisers assume that the highest bid guarantees ad visibility. In practice, Google uses ad rank to determine whether an ad is shown at all, not just its position on the page. Ad rank is calculated based on your bid, quality score, the expected impact of ad extensions and formats, and user context — including factors like device type, location, and time of search.
Winning an auction does not guarantee that your ad will appear. If the ad is not relevant or the landing page provides a poor experience, Google may choose not to show it, prioritizing user experience instead.
For example, a business running Google Ads saw their impressions decline sharply from 90,000 to 2,000 over a few months. The cause was a deterioration in landing page speed. Despite maintaining competitive bids, reduced site performance negatively affected their quality score and ad rank. After improving page load times, impressions recovered — highlighting how critical landing page experience is to campaign success.
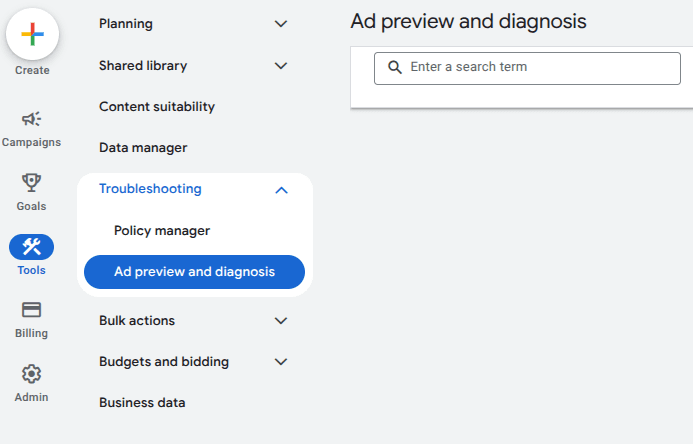
You can use the Ad Preview and Diagnosis Tool (found under Tools & Settings > Planning) to check ad eligibility for specific keywords, locations, and devices without affecting campaign performance or impressions.
2. How negative keywords improve campaign efficiency
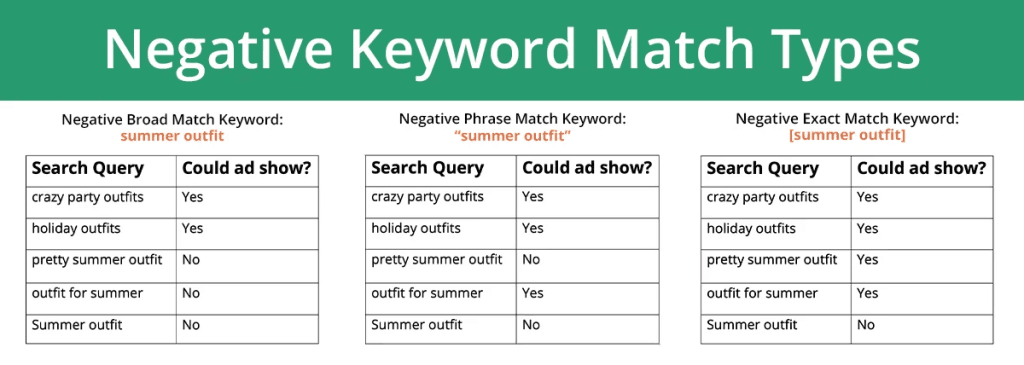
When ads appear for irrelevant search terms, they can lead to wasted spend and lower performance. Negative keywords help refine targeting by preventing ads from showing for searches that are unlikely to convert, improving clickthrough rates and overall lead quality.
Using negative keywords also helps reduce unnecessary impressions and directs budget toward higher-intent audiences. For example, a luxury wedding planner in New York found that their ads were appearing for terms such as “DIY wedding ideas” and “cheap wedding planning.” By adding negative keywords like “DIY,” “cheap,” and “budget,” they improved the quality of traffic, reduced unqualified clicks, and optimized ad spend.
How to update negative keywords:
- Review the search terms report regularly to identify irrelevant queries.
- In your campaign, navigate to keywords > negative keywords.
- Add negative keywords manually or upload a curated list.
3. Understanding ad rank beyond the bid
Ad rank is often misunderstood as being determined solely by bid amount. In reality, a lower bid paired with a strong user experience can outperform a higher bid with weaker relevance or site quality.
Key factors influencing ad rank:
- Bid amount
- Ad relevance (alignment between ad copy and user query)
- Landing page experience
- Expected clickthrough rate (CTR)
- Use of ad formats and extensions
By focusing on ad relevance, improving landing page load times, and aligning landing page content with user intent, it is possible to achieve higher ad positions without increasing your budget.
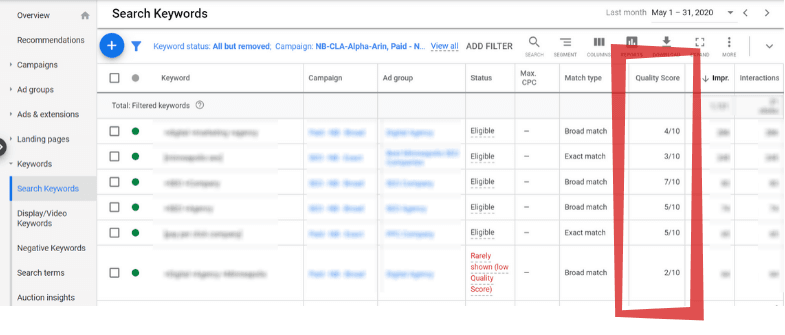
To support ongoing improvements, review the quality score for each keyword regularly. This can be done by adding the quality score column in Google Ads (found under “columns” > “modify columns” > “quality score”) and addressing any areas with low scores.
4. Excluding unprofitable locations
Running ads in the wrong locations can impact budget efficiency, particularly when targeting large regions or national audiences. Many advertisers overlook that selecting a geographic area in Google Ads also includes users who express interest in that location, even if they are not physically present. This can include users researching an area or browsing while traveling.
If specific cities, zip codes, or countries consistently deliver low conversion rates or high bounce rates, continuing to target them may not be a sound investment. Refining geographic targeting helps improve return on investment (ROI) and ensures that spend is directed toward areas with higher conversion potential.
In a case study by PPC Hero, a brand excluded ads from low-performing regions and measured a 20% improvement in ROAS within 30 days. By removing non-converting areas, they were able to reallocate budget to stronger-performing locations.
To exclude specific locations in Google Ads:
- Navigate to your campaign and select settings > locations > advanced search.
- Use the exclude option to block specific countries, cities, zip codes, or radii.
- Regularly review the geographic report in the locations tab to identify underperforming areas.
Additionally, adjust the location settings from the default “presence or interest” to “presence” only for more precise targeting.

5. Evaluating the value of branded keyword campaigns
Some advertisers are hesitant to bid on their own brand name, assuming organic rankings are sufficient. However, branded keyword campaigns can provide several strategic advantages:
- They typically have lower cost-per-click (CPC) due to high relevance and Quality Score.
- They often deliver stronger conversion rates, as brand-aware users tend to have higher intent.
- They help protect your brand from competitors bidding on your name and capturing potential customers.
Branded campaigns also offer greater control over your messaging. You can use them to promote limited-time offers, showcase testimonials, or highlight seasonal campaigns — aspects that are not easily customized within organic search results.
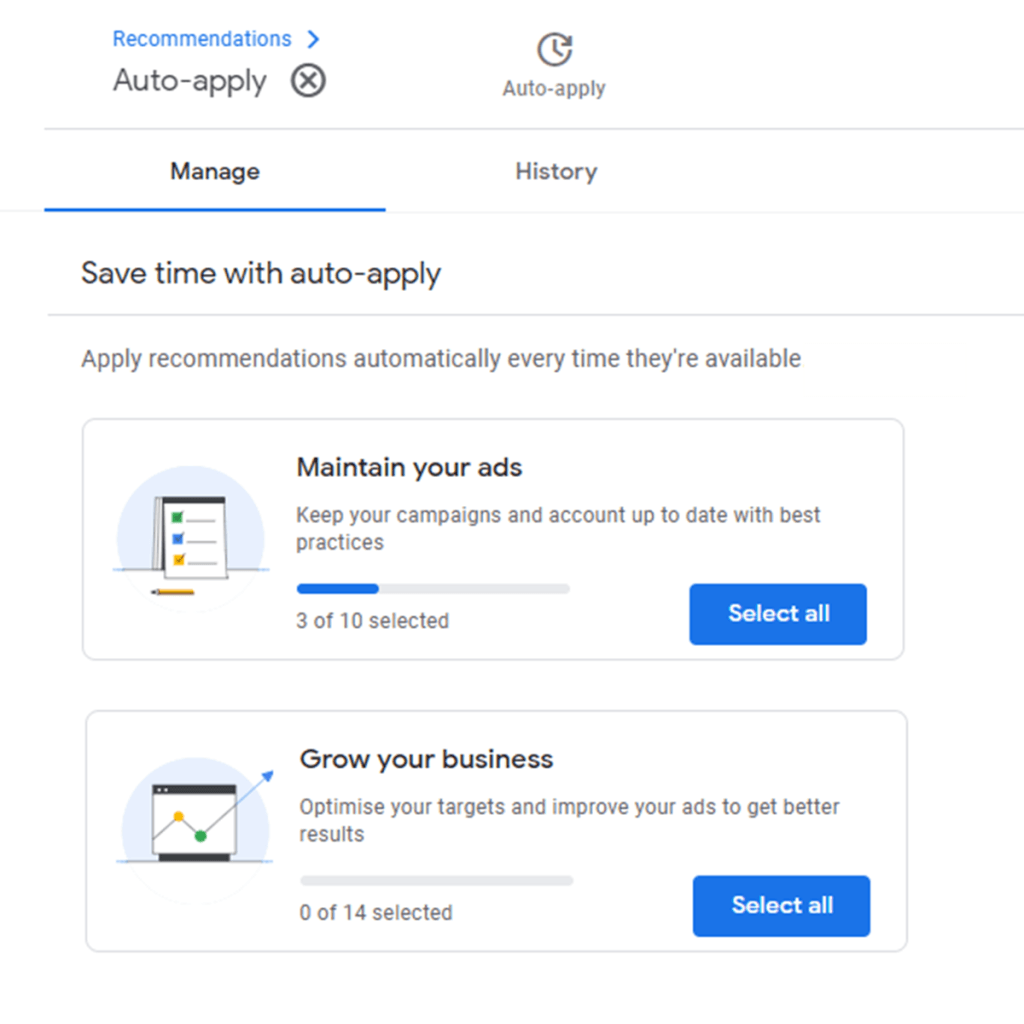
6. Why automated recommendations should be reviewed carefully
Google Ads provides optimization suggestions through the Recommendations tab, offering adjustments based on campaign performance and industry benchmarks. While some recommendations can be helpful — such as fixing disapproved ads or setting up conversion tracking — others may not align with business goals. Automatically applying all recommendations without review can negatively impact campaign performance.
Google’s AI-driven recommendations are designed to increase a campaign’s optimization score. However, some suggestions, like switching all keywords to broad match or raising daily budgets, may prioritize platform metrics over advertiser results.
It is important to note that Google now auto-applies certain recommendations unless you manually opt out. Changes can occur without explicit review unless this setting is adjusted.
Common recommendations to review carefully:
- Switching to broad match: May increase irrelevant traffic without strong negative keyword strategies in place.
- Raising budgets: Increasing spend without demonstrated performance improvements can reduce efficiency.
- Adding irrelevant keywords: Automatically suggested keywords may not reflect campaign intent, especially in niche industries.
- Removing low-volume keywords: Long-tail keywords with low volume can often be high-converting and should not be removed without analysis.
For example, in a case study shared by Grow My Ads, an ecommerce business experienced a significant rise in irrelevant traffic after auto-applied broad match recommendations. Their clickthrough rate declined, CPC increased by 35%, and budget was spent inefficiently until the settings were manually corrected.
Best practices for managing recommendations:
- Review all recommendations manually on a regular schedule (weekly or biweekly).
- Opt out of auto-apply features:
- Navigate to settings > account settings > auto-apply recommendations.
- Deselect recommendations that do not align with your strategy.
- Prioritize suggestions focused on:
- Fixing disapproved ads or broken URLs
- Implementing relevant ad extensions
- Improving ad copy variety
Optimization score does not equal business success
A high optimization score is not the goal. A score of 75% or 80% can be sufficient if campaigns are performing effectively. The focus should remain on profitability and achieving campaign objectives, not simply raising the optimization score.
7. Scheduling ads by time, device, and conditions
While many advertisers use basic ad scheduling — selecting specific days and hours for campaigns — fewer take advantage of more advanced controls like time-of-day, device-specific targeting, and real-world condition triggers.
Used strategically, these methods can improve efficiency by ensuring ads are shown when and where they are most likely to perform well, minimizing wasted spend and increasing conversions.
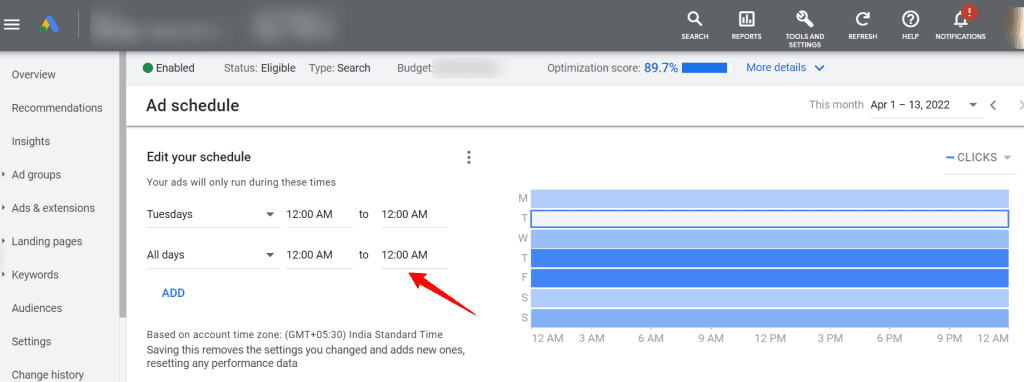
Time-of-day and day-of-week targeting
This feature allows ads to run only during business hours, peak shopping periods, or when sales teams are available to handle inquiries. It is particularly effective for local businesses, B2B companies, and service providers with defined operating hours.
How to set it up:
- Navigate to your campaign and select Settings > Ad Schedule.
- Choose custom days and hours for ad delivery.
- Analyze performance trends using the Segment > Time view.
Device-level scheduling
Google Ads supports bid adjustments by device (desktop, mobile, tablet), enabling advertisers to tailor bids based on user behavior patterns. For example, a SaaS company observed that demo sign-ups were higher from desktop users during weekdays. In response, they reduced mobile bids on weekends and doubled their desktop presence Monday through Friday from 8 AM to 6 PM.
This strategy, combined with conversion tracking data, helps ensure that budgets are allocated where conversion potential is highest.
To adjust:
- Navigate to Campaign > Devices > Set bid adjustments to increase or decrease bids by device type.
Weather-based scheduling (using third-party tools)
Google Ads does not natively support weather-based targeting. However, third-party tools such as WeatherAds allow advertisers to trigger ads based on local weather conditions, including rain, temperature drops, or UV index levels.
For example, an HVAC repair company used WeatherAds to increase bids when local temperatures dropped below 40°F. Their cost-per-lead decreased by 35% during cold snaps, aligning ad spend with peak demand periods.
Weather-based triggers are especially useful for:
- Clothing brands (e.g., promoting rainwear during storms)
- Event venues (e.g., pausing outdoor event ads on rainy days)
- Auto repair or HVAC services
- Health and skincare products (e.g., sunscreen ads during sunny periods)
Key takeaways
Consider tools like WeatherAds to make campaigns responsive to external conditions.
Use Ad Schedule to focus budget on times when performance is highest.
Adjust bids by Device to align spend with conversion behavior.
8. Wait for enough data before turning on Smart Bidding
Smart Bidding strategies like Target CPA, Maximize Conversions, or Target ROAS rely on machine learning — but they need real data to work. Without it, performance can become unpredictable, and ad spend gets wasted.
Google’s algorithm works best when it has enough historical conversion data to learn from. If you activate Smart Bidding too early, you risk confusing the system. It may optimize for the wrong signals or simply underperform.
A case study by DataFeedWatch illustrates this. A Swedish kitchenware brand, KitchenLab, refined its product feed before switching to Smart Bidding. They improved ROAS by 46% over three months by:
- Improving product titles (adding brand, size, and color)
- Categorizing products by profit margin using custom labels
This also led to a 35% drop in ad costs and an 18% boost in traffic — all by giving Google better data to work with.
When to switch to Smart Bidding:
- After at least 30 conversions for Target CPA
- At least 50 conversions for Target ROAS
- With 2–4 weeks of consistent performance
Rushing into automation without enough signal won’t save time — it will just burn budget.
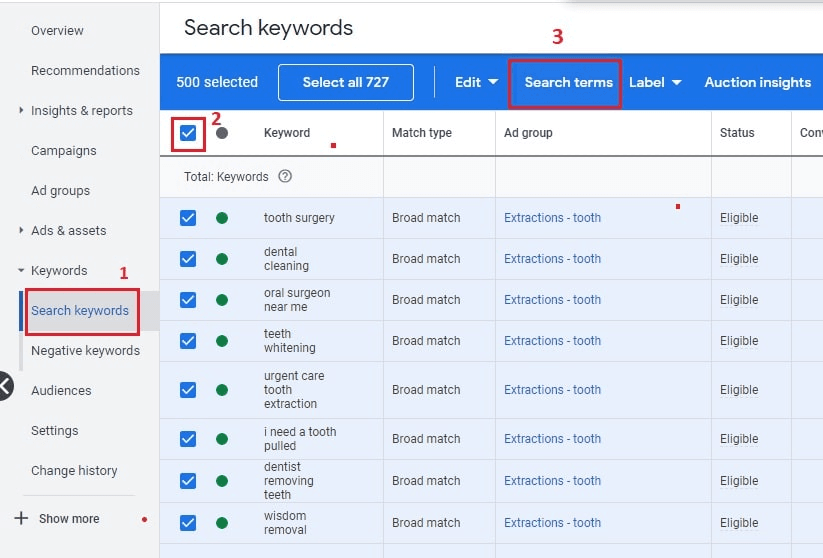
9. Use Search Terms to improve targeting
The Search Terms report shows exactly what people typed into Google before they saw your ad. It’s one of the most useful tools in Google Ads.
It helps you:
- Uncover new keyword opportunities
- Add negative keywords to filter out irrelevant traffic
- Understand user intent behind the clicks
A photography studio saw dozens of searches for “wedding photographer near me cheap.” They excluded “cheap” and added “affordable wedding photographer” — and doubled their conversions.
How to do it:
- Go to Keywords > Search Terms
- Filter by conversions, CTR, or spend
- Use the results to refine targeting and rewrite your ad copy
The data inside this report will tell you whether your ads are reaching the right audience — or wasting budget.
10. Preview ads without inflating impressions
Don’t Google your own keywords to check if your ad is live. It doesn’t just waste time — it damages your ad performance.
Every time you search but don’t click, Google logs it as an impression with no engagement. That drags down your CTR and hurts your Ad Rank.
Here’s how to do it right:
Use the Ad Preview and Diagnosis Tool (found under Tools & Settings > Planning). It shows whether your ad is showing — without impacting performance.
You can preview by:
- Device
- Location
- Language
- Keyword
Bonus: it also helps you figure out why an ad might not be appearing. No more guessing.
Conclusion
Running effective Google Ads campaigns means taking full control of how your budget is spent. That includes where your ads appear, who sees them, when they’re shown, and what queries trigger them.
Features like keyword targeting, ad scheduling, location exclusions, Smart Bidding thresholds, and negative keyword filters exist for a reason. They’re not optional — they’re essential for campaigns that aim to be efficient, not expensive.
If campaigns are underperforming, the problem often isn’t the budget — it’s how the account is configured. Poorly matched search terms, broad location settings, or premature automation can quietly waste thousands.
Review each area covered in this guide. Audit your current setup. Fix what isn’t aligned with your actual goals. These aren’t big changes, but they have a measurable effect.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Why is my Google ad not showing even though I’m bidding high?
Google considers more than just your bid. Your ad may not show due to low Quality Score, poor landing page experience, limited budget, or negative keywords that block it. Use the Ad Preview and Diagnosis Tool to troubleshoot.
Q2: What’s the difference between broad, phrase, and exact match types – and which is best?
Broad match: shows for related searches, often too vague
Phrase match: shows when query contains your phrase in order
Exact match: shows only for the exact keyword (or close variants)
Best practice: Start with phrase and exact for more control. Use broad match cautiously, and monitor with the Search Terms Report.
Q3: How do I know if Smart Bidding is working?
Track your campaign’s Target CPA, ROAS, and conversion rates. Give it 2–4 weeks after activation, with enough historical data. Expect gradual improvements, not overnight miracles.
Q4: Can I run ads in certain areas of a city but exclude others?
Yes! Use Advanced Location Settings to include or exclude specific zip codes, neighborhoods, or radiuses. Use location performance reports to spot underperforming areas and block them.
Q5: How do I make sure Google’s recommendations don’t mess up my campaign?
Go to the Recommendations tab, review each one manually, and dismiss anything that doesn’t align with your goals. Avoid applying “Enable broad match” or “Raise budgets” blindly.
Q6: Is it okay to click on my own ad to check if it works?
No. Clicking your own ad wastes budget and disrupts performance data. Instead, use the Ad Preview and Diagnosis Tool to check ad visibility safely.