Table of Contents
What are phishing scams and how do they work?
A phishing scam is when a scammer pretends to be someone you trust, like your bank or a popular website, to trick you into giving up personal info, clicking a fake link, or downloading something nasty.
Online fraud is everywhere these days, and phishing scams are among the sneakiest tricks scammers use. They work by pretending to be legitimate organizations – banks, streaming services, social media platforms, or even your workplace – to trick you into handing over sensitive information like passwords, credit card numbers, or personal details.
As digital communication has grown, so have these scams. They’re no longer limited to sketchy emails full of spelling mistakes. Now, phishing attempts appear on social media, messaging apps, and even fake customer support chats. Some scams are so well-crafted that even tech-savvy users can fall for them.
So, how do these phishing scams actually work? It all comes down to psychological manipulation. Scammers rely on emotions like fear, urgency, and curiosity to push people into making hasty decisions. Ever received an email saying, “Your account has been compromised! Click here to reset your password immediately!”? That’s urgency at play. Or maybe you got a message saying, “Congratulations! You’ve won a free iPhone!”—that’s tapping into curiosity and excitement. The goal is to make you act fast before you have time to think critically.
Understanding these tactics is the first step in protecting yourself. In the next sections, we’ll break down common phishing scams, how to recognize them, and what you can do to stay safe online.
How scammers operate?
Phishing scams aren’t just random spam emails; they’re carefully designed traps meant to exploit human psychology and trust. Scammers use a variety of tactics to get people to lower their guard and hand over sensitive information. Here’s how they do it:
- Urgency tactics: One of the most common tricks in a scammer’s playbook is creating a false sense of urgency. You might get an email claiming, “Your account will be suspended in 24 hours unless you verify your identity!” or “Suspicious activity detected – log in immediately to secure your funds!” The goal is to make you panic and take action without questioning the legitimacy of the request. If something demands immediate action, take a step back. Legitimate companies don’t pressure you like this, and you can always verify the claim by contacting the company directly through official channels.
- Fake links: Scammers are masters at deception, and one of their most effective tools is fake websites. You might receive a link that appears to lead to your bank, email provider, or a popular online store, but in reality, it’s a carefully crafted clone designed to steal your login details. These fake sites often have small but crucial differences in their URLs – like “yourbank-secure.com” instead of “yourbank.com.” Once you enter your credentials, the scammer instantly captures them and can access your real account. Tip: Always hover over links (on a computer) or long-press them (on mobile) to see where they actually lead before clicking.
- Malicious attachments: Not all phishing scam attempts try to steal passwords directly—some aim to infect your device with malware. These scams often come in the form of email attachments that claim to be invoices, receipts, or important documents. Once opened, the attachment can install ransomware (locking your files until you pay a ransom), spyware (tracking your keystrokes and stealing sensitive data), or trojans (which allow hackers to take control of your system). A good rule of thumb: If you weren’t expecting an attachment, don’t open it—especially if it comes from an unknown sender.
- Social engineering: Sometimes, scammers don’t need advanced tech tricks – they just need to sound convincing. Social engineering scams involve scammers pretending to be someone you know or trust, like your boss, a coworker, or even a family member. You might get an email from “your CEO” urgently requesting gift card codes or a message from “your friend” asking for money because they’re stranded abroad. Scammers also hijack real accounts and message contacts directly, making the scam seem even more legitimate. If a request seems unusual, verify it through another method—like calling the person directly.
Understanding these methods is the first step in safeguarding yourself. Scammers rely on deception and emotional manipulation, but by staying cautious and double-checking unexpected messages, you can outsmart them. Next, we’ll explore real-life examples of phishing scams and how to spot them before it’s too late.

Diagram showing a phishing email with highlighted red flags (e.g., fake links, spelling errors)
How to recognize a typical phishing attempt?
Ask yourself, “Is this email/message legitimate?” If you even have to hesitate, there’s a good chance it’s not. Scammers are skilled at making their messages look convincing, but if you know what to look for, you can spot the red flags before falling into their trap.
Red Flags to look out for:
- Sender address: Scammers love to imitate official organizations, but their email addresses often have subtle (or not-so-subtle) mistakes. Instead of getting an email from support@paypal.com, you might see something like: supp0rt@paypa1.com (using a zero instead of “o” or a “1” instead of “l”)
- Urgent language: Phishing emails often try to scare you into acting fast. Common phrases include: Your account has been compromised! Change your password immediately!” Legitimate companies rarely use scare tactics like these. If an email is trying to rush you into clicking a link, stop and verify before doing anything.
- Generic greetings: Most legitimate companies address you by your name, but scammers often don’t have that information. Instead, they use generic greetings like: “Dear customer” or “Dear user”. If a company you actually do business with suddenly stops using your name, that’s a major red flag.
- Suspicious attachments: Scammers often include links or attachments that can steal your information or infect your device. Be wary of: Unexpected attachments, especially files ending in .exe, .zip, .scr, or .js (these can contain malware) and fake links—hover over them (on a computer) or long-press them (on mobile) to see where they actually lead before clicking.
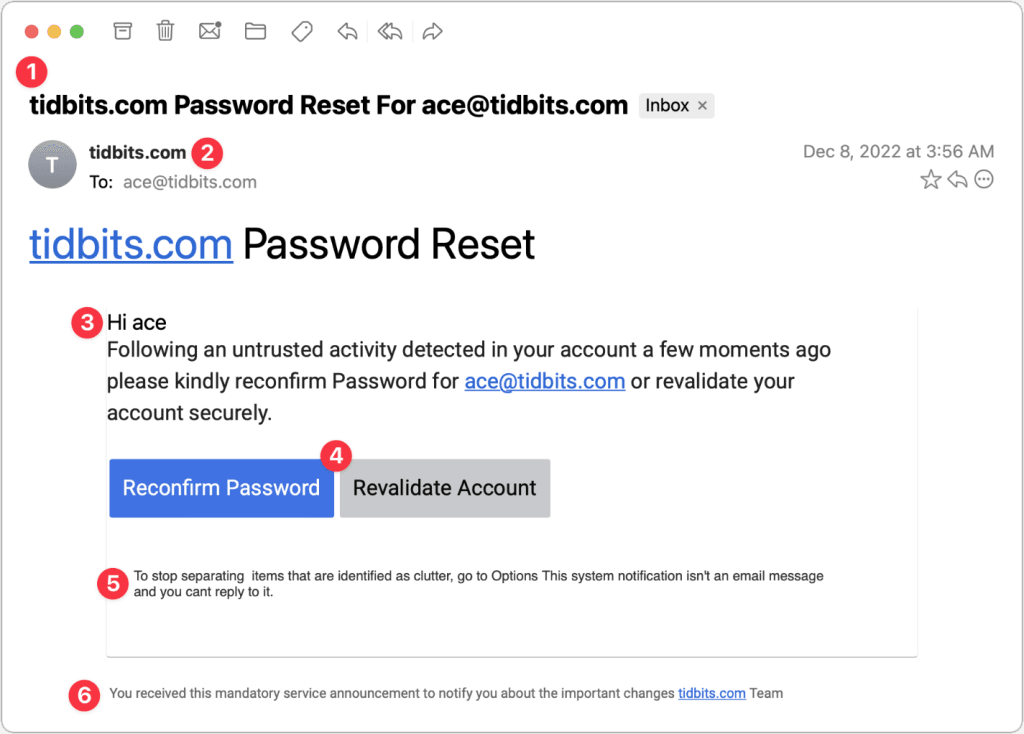
Screenshot of a phishing email with indicators pointing out suspicious elements
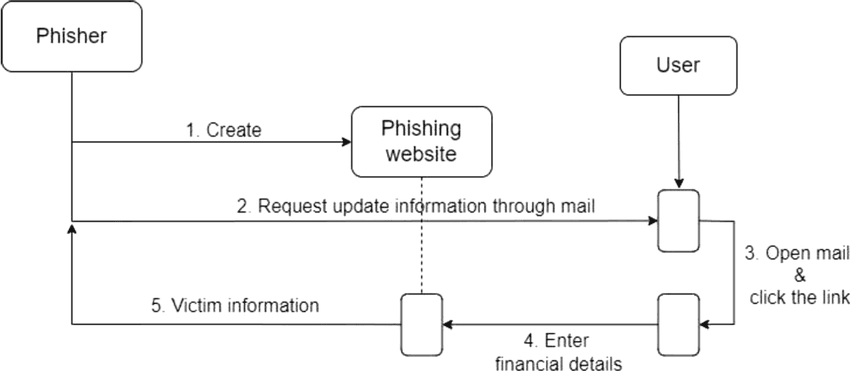
What happens if you click a phishing link?
Clicking on a phishing scam link isn’t just a minor mistake – it can have serious consequences. Scammers are constantly refining their tactics, and even a single click can open the door to a range of threats. Here’s what could happen:
- Identification as a target: Ever wonder why some people seem to get bombarded with scam emails and messages? If you click on a phishing link, even if you don’t enter any information, scammers may flag you as a responsive target. This means you could receive even more phishing attempts, since they know you’re likely to engage. Think of it like junk mail – once one scammer gets a response, they spread the word, and suddenly, you’re on every scammer’s list.
- Device compromise: Many phishing links don’t just try to steal your login credentials – they can also download malware onto your device. If your computer suddenly slows down, starts acting weird, or you notice files disappearing, it could be a sign that malware has been installed.
- Data theft: The most common outcome of clicking a phishing link is landing on a fake website that looks like a real one – your bank, PayPal, or even Google. If you enter your credentials, they’re instantly sent to the scammer.
- You lose access to your account: For digital marketers, influencers, or anyone managing online accounts, a phishing attack can be devastating. This is especially dangerous for people who manage multiple accounts or handle sensitive client information.
- Financial loss: If scammers get access to your financial accounts, they can: Make unauthorized purchases with your saved payment details; Transfer money out of your bank accounts; Use your information to commit fraud or open new accounts in your name. In some cases, even if you act quickly, you may not get your money back—especially if the scam involves cryptocurrency or gift cards.
Flowchart showing the potential fallout from clicking a phishing link
How to protect yourself from phishing scams?
Phishing scams are getting more sophisticated, but that doesn’t mean you have to fall for them. A little caution and the right habits can go a long way in keeping you safe online. Here are some essential tips to help you stay ahead of scammers:
- Verify links: Use online link checkers to determine a URL’s safety before clicking. Hover over the link to view the full URL before clicking.
- Check sender details: Look closely at email addresses for subtle errors. Scammers often use domains that look similar to legitimate ones.
- Adopt a suspicious mindset: Assume links from unknown senders are malicious until proven otherwise.
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA): Adds a second layer of security to your accounts. Even if your credentials are compromised, 2FA can prevent unauthorized access.
- Use antivirus software: Regular scans can detect and prevent malware infections. Keep your software updated to stay protected against the latest threats.
- Educate yourself: Stay informed about the latest phishing techniques and scams. Awareness is one of the most effective defenses.

Checklist graphic summarizing the above points. Source: FasterCapital
While good habits go a long way in preventing phishing scam attacks, the right tools can add an extra layer of security to your online life. Here are some must-have tools to help keep scammers at bay:
- Online link checkers: Before clicking a suspicious link, run it through an online link checker to verify its legitimacy. These tools analyze URLs and flag known phishing sites. We recommend tools like Google Safe Browsing and Phish Tank.
- Password managers: One of the biggest mistakes people make is reusing weak passwords across multiple accounts. A password manager helps by generating strong and unique passwords for every account and also storing them securely, so you don’t have to remember them.
- Email filters: Phishing emails often slip through standard spam filters, but advanced filtering tools can catch them before they reach your inbox. Use AI-powered spam filters – services like Gmail, Outlook, and ProtonMail have built-in phishing detection. If an email looks suspicious but isn’t in your spam folder, report it as phishing to help improve email security for everyone.
Real-life examples of phishing attempts
Phishing scams aren’t just theoretical threats – they happen every day, targeting individuals and businesses alike. Let’s look at a real-world case study and some emerging phishing threats you should be aware of.
Case study: A digital marketer falls for a phishing scam
Scenario:
A digital marketer receives an urgent email from what appears to be Facebook Ads Support warning about “unusual account activity.” The email states that if immediate action isn’t taken, their ad account will be suspended.
The marketer, worried about losing access to ad campaigns, clicks the link and logs in – unfortunately, on a fake Facebook login page. Within minutes, scammers gain full access to the account, change passwords, and begin running fraudulent ads using the marketer’s budget.
Outcome:
- The scammer burns through ad spend, running unauthorized ads.
- The marketer loses access to their business account.
- Clients’ data and advertising funds are at risk.
Recovery:
Fortunately, the marketer acted quickly:
- They contacted Facebook Support and reported the hack.
- They reset their password and secured their email account.
- They enabled two-factor authentication (2FA) to prevent future breaches.
This case highlights how easy it is to fall for a phishing scam, especially when urgency is involved.
these phishing emails are getting better by the day
— Ananay Batra (@ananbatra) February 8, 2025
almost fell for it pic.twitter.com/3nSP5u4qxQ
Emerging phishing threats
Scammers are constantly adapting their tactics, moving beyond emails to target people through text messages, phone calls, and social media messages. Here are some of the most common phishing scam threats today:
SMS phishing (smishing)
Instead of using email, scammers send fraudulent text messages that include malicious links. These messages often claim to be from:
- A bank, warning of a locked account and requesting immediate action.
- A delivery service, stating that a package is delayed and needs verification.
- A government agency, threatening legal action due to unpaid taxes.
How to stay safe: Never click on links in unexpected text messages. If you receive a concerning message, visit the official website directly or contact customer support.
Voice phishing (vishing)
Scammers call their victims pretending to be from a bank, government agency, or tech support team. Their goal is to trick people into revealing sensitive information over the phone.
Common vishing scams include:
- Fake bank fraud alerts asking for personal details.
- IRS or tax agency scams threatening legal action unless payment is made immediately.
- Tech support scams claiming a computer has been infected with a virus and requires remote access.
How to stay safe: Hang up and call the company directly using their official phone number. Never provide sensitive information over the phone unless you initiated the call.
Social media scams
Scammers use fake profiles or compromised accounts to impersonate brands, influencers, or even close friends on social media platforms.
Common social media scams include:
- Fake giveaways: “Congratulations! You’ve won! Click this link to claim your prize.”
- Messages from “friends” asking for money, often due to their account being hacked.
- Job or investment scams that promise high returns but require an upfront payment.
What happens now and what can we do about preventing further phishing attempts?
Phishing scams are only getting more common as we spend more time online. It can feel like a constant battle to stay ahead of scammers, but the good news is that by staying aware and adopting a few simple habits, you can significantly reduce your chances of falling for one.
Cybercriminals are always changing things up, coming up with new ways to trick people. They send out more convincing emails, set up fake websites, and even make phone calls to get you to share sensitive info. That’s why it’s so important to stay on top of the latest scams and be able to spot the red flags before it’s too late.
Businesses also have a part to play in keeping phishing attempts at bay, like using stronger security measures (think multi-factor authentication) and training their employees to spot scams. On your end, just taking a few simple steps – like double-checking who’s sending an email, steering clear of dodgy links, and using strong, unique passwords – can really make a difference. Phishing scams might never completely go away, but by staying aware and using smart online habits, you can definitely cut down the risk.
Key takeaways
- Scammers thrive on urgency, fake links, and manipulation – they want to get you to act quickly and without thinking.
- Clicking on phishing links can lead to big problems, from malware to identity theft and financial loss.
- Simple steps like verifying links, using 2FA, and having strong passwords can make a huge difference.
- New phishing scam tactics, like smishing (SMS phishing) and vishing (phone phishing), are becoming more common, so stay on alert.
- Knowledge is power! The more we educate ourselves and others, the harder it is for scammers to succeed.
Staying safe online doesn’t have to be complicated. By staying aware and practicing some smart habits, you can protect yourself from phishing scams. And the best part? You’re not just protecting yourself – you’re helping to create a safer online world for everyone.





